Credit
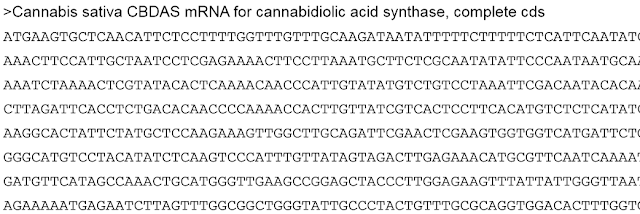
The large datasets received from a sequencing facility require special file types to organize information in an efficient and detailed manner. Additionally, the manipulation and analysis of this orginal file type will create other files that may not be encountered during everyday computer use. One of the most basic genomic file types is called a Fasta file, since the file will have the extension FileName.fasta. This file type is mainly used to have a string of nucleotides in the order they appear in the genome under a line of text that names that sequence. A fasta file can contain one or more sequences depending on the data the programmer is analyzing. An example of this file is shown below:
Another file type with a similar name is the Fastq file. This file contains more information than the simple Fasta file shown above since it not only contains the sequence but also a quality score associated with that sequence. In simple terms, this quality score describes how sure the sequencer was when labeling a location as a certain base.
The fastq format follows a specific pattern, which may seem difficult at first but can be broken down to the following pattern:
1. Header line starting with @
2. DNA Sequence
3. Spacer line starting with +
4. Sequence quality scores ususally in an unreadable format.
An example of a Fastq file is shown below:
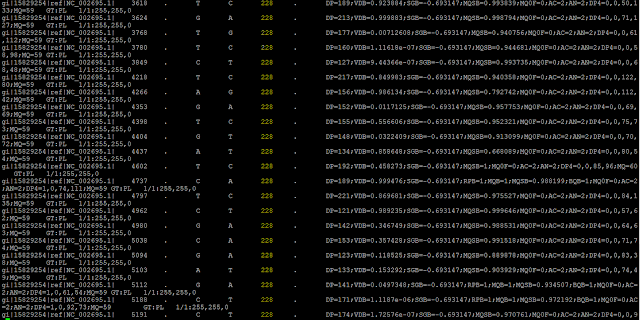
A VCF (Variant Call Format) File is extremely useful when determining the differences between the organism under study and a reference organism. This file type is formatted as a table that will show the SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) and INDELS (Insertions and Deletions) and the location they occur. Additionally, it shows how likely that difference is to be true with the attachment of another type of quality score shown in the highlighted column below. Every set of two lines contains an identifying tag on the first line and the difference that was noted on the following line. The table format that is created allows for certain columns to be called that filter out poor reads and mutations that arose from sequencing error and not a difference in the genome. An example of a VCF table only showing SNP's with a high quality score (228) are shown below:

Comments
Post a Comment